What Is Cross-Docking and How Can It Improve Delivery Speed?

In today’s hyper-competitive global supply chain, delivery speed is often the difference between satisfied customers and lost sales. For businesses aiming to optimize their logistics performance, one solution is gaining traction: cross-docking. This technique enables faster product movement, reduces warehouse costs, and ensures time-sensitive goods get to market quicker.
But what exactly is cross-docking, and how does it benefit importers, exporters, and sourcing agents? In this article, we’ll explore how cross-docking works, why it’s growing in popularity, and how BestSourcing-Agent.com can help you implement cross-docking strategies effectively in Asia and beyond.
What Is Cross-Docking?
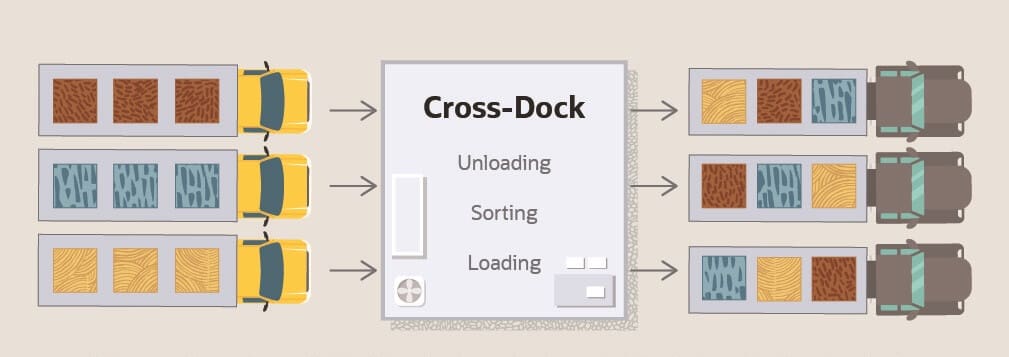
Cross-docking is a supply chain logistics strategy in which goods are received at a warehouse or distribution center and then immediately transferred to outbound transportation, with minimal or no storage time in between.
Instead of sitting in inventory for days or weeks, products are sorted, consolidated (if needed), and loaded onto delivery trucks bound for retail stores, fulfillment centers, or end customers.
Types of Cross-Docking:
-
Pre-Distribution Cross-Docking: Supplier-sorted items are shipped directly to specific destinations.
-
Post-Distribution Cross-Docking: Goods are sorted at the dock according to real-time demand or destination after arrival.
🔗 Learn more about warehouse optimization:
Agent-Managed Warehousing: Is It Worth It?
How Cross-Docking Works: A Simplified Example
Let’s say your business imports 10,000 phone accessories from China to Malaysia. Instead of storing the goods in a warehouse:
-
The shipment arrives at a cross-docking facility.
-
Items are scanned and sorted by destination.
-
The goods are loaded directly onto regional trucks headed for multiple retail stores across Southeast Asia.
The entire process may take less than 24 hours, cutting weeks off the typical delivery timeline.
Benefits of Cross-Docking in Global Logistics
✅ 1. Faster Delivery Times
By eliminating storage time, businesses can fulfill orders faster, meeting the growing demand for same-day or next-day delivery, especially in e-commerce.
🔗 Related: How to Handle Port Congestion Without Losing Inventory
✅ 2. Reduced Warehouse Costs
Cross-docking minimizes the need for long-term warehousing, significantly cutting down on:
-
Storage fees
-
Labor costs
-
Equipment requirements
This is particularly beneficial for seasonal goods or fast-moving consumer products.
✅ 3. Improved Inventory Turnover
With faster product flow, businesses achieve better inventory turnover rates, reducing the risk of:
-
Overstocking
-
Obsolescence
-
Damaged goods
🔗 Explore: Scaling Logistics Operations During Seasonal Spikes
✅ 4. Streamlined Last-Mile Delivery
Cross-docking can be used to consolidate smaller shipments heading to the same region, leading to more efficient last-mile delivery—often the costliest part of logistics.
🔗 Read next: Multimodal Transport Enhances Resilience
When Is Cross-Docking the Right Strategy?
Cross-docking is not ideal for every product or supply chain. It works best when:
-
Products are pre-packaged and barcoded.
-
There’s predictable or high-volume demand.
-
Goods are perishable or time-sensitive.
-
A company has a centralized distribution plan.
Industries that benefit include:
-
Retail and fashion
-
Automotive parts
-
Consumer electronics
-
Pharmaceuticals
-
Food and beverage
🔗 Related: Temperature-Controlled Logistics for Perishable Exports
Common Cross-Docking Challenges
While advantageous, cross-docking also has operational hurdles:
-
Requires high coordination among suppliers, carriers, and distributors.
-
Demands accurate data and real-time tracking.
-
Needs a network of strategically placed distribution points.
This is why many businesses turn to local sourcing agents to ensure efficient execution.
How Sourcing Agents Enhance Cross-Docking Efficiency
A trusted sourcing agent can:
-
Pre-arrange dock schedules with local partners
-
Conduct quality control before loading onto outbound trucks
-
Verify correct customs documentation
-
Manage carrier coordination and delivery tracking
With boots on the ground, sourcing agents bridge the gap between manufacturers, logistics providers, and buyers.
🔗 More on QC: Post-Production Inspection: Agent vs. Third Party
Why Choose BestSourcing-Agent.com for Cross-Docking Solutions?
At BestSourcing-Agent.com, we specialize in optimizing international supply chains for speed and cost-efficiency. Through our strategic partnerships across Asia—including China, Vietnam, Cambodia, and Malaysia—we can set up cross-docking hubs near your suppliers, ensuring minimal delay and maximum inventory control.
Our cross-docking services include:
-
Dock-to-dock transfer operations
-
Real-time shipment tracking
-
Customs clearance and inspection
-
Last-mile delivery coordination
Whether you’re shipping electronics from Shenzhen or textiles from Ho Chi Minh City, we ensure your goods reach their destination faster and smarter.
Final Thoughts
Cross-docking is more than just a logistics buzzword—it’s a proven method for improving speed, reducing costs, and gaining a competitive edge in international trade. By bypassing warehouse delays and optimizing freight flow, businesses can meet today’s just-in-time delivery expectations.
However, implementing cross-docking effectively requires expert coordination, local insight, and real-time communication. That’s where BestSourcing-Agent.com comes in. With years of experience managing supplier relationships and logistics in Asia, we help clients scale faster, smarter, and with less risk.
✅ Ready to streamline your logistics with cross-docking?
Contact BestSourcing-Agent.com to speak with a cross-border logistics expert today.