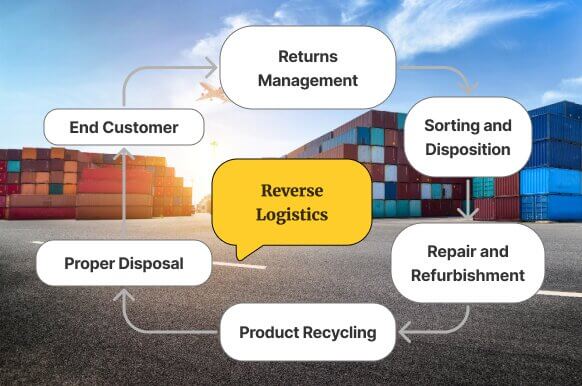
How Reverse Logistics Supports Circular Sourcing
As global supply chains evolve in response to climate challenges, economic pressures, and consumer demand for sustainability, reverse logistics has emerged as a key enabler of the circular sourcing economy. Rather than ending at delivery, modern logistics systems now manage the return, reuse, recycling, and repurposing of goods—transforming waste into value.
In this blog, we explore how reverse logistics empowers circular sourcing, the benefits for sourcing agents and businesses, and what strategies are shaping the future of sustainable trade.
What Is Reverse Logistics?
Reverse logistics refers to the processes involved in moving goods from the end customer back to the seller or manufacturer. This includes:
-
Product returns
-
Recycling or refurbishment
-
Warranty recovery
-
Unsold inventory returns
-
End-of-life take-back programs
Unlike forward logistics (production to consumption), reverse logistics travels upstream and is often more complex due to product condition variability, disassembly needs, or environmental compliance.
🔗 Learn more about logistics evolution in Freight Futures and Predictive Trade Analytics
What Is Circular Sourcing?
Circular sourcing is part of the broader circular economy—a system designed to eliminate waste and maximize resource efficiency. In sourcing, this means:
-
Choosing materials that can be reused, repaired, or recycled
-
Designing products with multiple life cycles in mind
-
Working with suppliers and agents to close the loop on production
Sourcing agents play a central role in circular sourcing by identifying suppliers aligned with these principles and managing reverse supply chains.
🔗 Explore: The Future of Sustainable Logistics in Sourcing
How Reverse Logistics Supports Circular Sourcing
1. Enabling Resource Recovery
Through reverse logistics, companies retrieve used products or components from customers or retailers. These materials are then:
-
Reused in new production
-
Refurbished and resold
-
Recycled into raw materials
Agents who manage reverse flows help ensure that materials retain their value, reducing dependency on virgin resources.
2. Boosting Transparency and Traceability
Sourcing agents and logistics providers now use IoT and blockchain to track materials as they re-enter the supply chain. This visibility allows companies to:
-
Monitor component reusability
-
Verify supplier compliance with sustainability goals
-
Prove ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) performance to stakeholders
🔗 Related: Blockchain in Freight Documentation: The New Norm?
3. Supporting Ethical and Eco-Friendly Brand Positioning
With circular logistics in place, companies can back up their sustainability claims with actions. Through reverse logistics channels, brands can:
-
Offer take-back or recycling programs
-
Reduce landfill waste
-
Engage customers in circular practices
Sourcing agents with sustainability expertise can guide these programs, enhancing brand credibility in global markets.
4. Creating Localized Collection and Processing Hubs
Sourcing agents help identify regional partners who can:
-
Collect and sort returned goods
-
Disassemble and process parts
-
Repackage or reintroduce salvaged materials into local production
This localized loop reduces transportation emissions and shortens the resource recovery cycle.
🔗 Recommended: Agent-Managed Warehousing: Is It Worth It?
5. Reducing Total Cost of Ownership
Though reverse logistics requires upfront investment, it can reduce overall costs by:
-
Cutting waste management fees
-
Lowering material procurement expenses
-
Generating revenue from resale/refurbishment channels
Agents with reverse supply chain knowledge help identify profitable recovery strategies and streamline operations.
Examples of Circular Reverse Logistics in Action
| Industry | Circular Practice | Reverse Logistics Role |
|---|---|---|
| Apparel | Clothing take-back and fiber recycling | Sorting, quality check, fiber recovery |
| Electronics | Repair and resale of used devices | Component testing, repair logistics |
| Furniture | Disassembly and reconfiguration | Storage, reverse transport, refurbishment |
| Packaging | Reusable crate systems | Return logistics, sterilization, redistribution |
Challenges in Implementing Reverse Logistics for Circularity
While the benefits are substantial, several challenges exist:
-
Infrastructure gaps in emerging markets
-
Inconsistent return volumes complicating logistics planning
-
Contamination risks during material recovery
-
Customer participation barriers
This is where professional sourcing agents add value. By offering on-ground support, language translation, and supplier vetting, they help businesses navigate these barriers.
🔗 See also: How to Vet Third-Party Logistics Providers
Role of Sourcing Agents in Circular Reverse Logistics
Sourcing agents facilitate circular reverse logistics through:
-
Supplier assessment for circular compatibility
-
Local partnerships for recovery, repair, and reprocessing
-
Coordination of multimodal transport for return flows
-
Documenting and reporting circular performance to clients
By acting as logistical coordinators, compliance monitors, and circular economy advocates, sourcing agents help businesses build greener, leaner, and legally compliant sourcing models.
🔗 Related reading: How Multimodal Transport Enhances Resilience
Final Thoughts
In a world shifting toward climate responsibility and resource efficiency, reverse logistics is no longer a “nice-to-have”—it’s essential. It not only supports circular sourcing but builds resilience, saves money, and strengthens brand value.
Companies aiming to achieve their sustainability targets should invest in sourcing agents who understand reverse flows, recovery economics, and circularity at scale.
Why Work with Bestsourcing-agent.com?
Our experienced sourcing agents help brands:
-
Integrate reverse logistics into global supply chains
-
Manage local returns and recycling hubs
-
Source sustainable materials and partners
-
Align with ESG and circular economy frameworks
👉 Contact us today to make your sourcing model circular and future-ready.